Editor’s Note: This piece was originally published in 2014. In April 2020, it was revised to include updated product information and links, mirrorless zoom lens information etc.
What is a Zoom Lens?
A zoom lens is a type of camera lens that offers the photographer a useful range of different focal lengths in a single lens. This is in comparison to a prime lens, which only offers a single focal length. A zoom lens allows for quick and easy re-framing of a scene while staying in the same physical position. SIGMA offers a wide variety of zoom lenses, ranging from wide-angle zooms, super telephoto zoom lenses, and standard zoom lenses designed for everyday use.
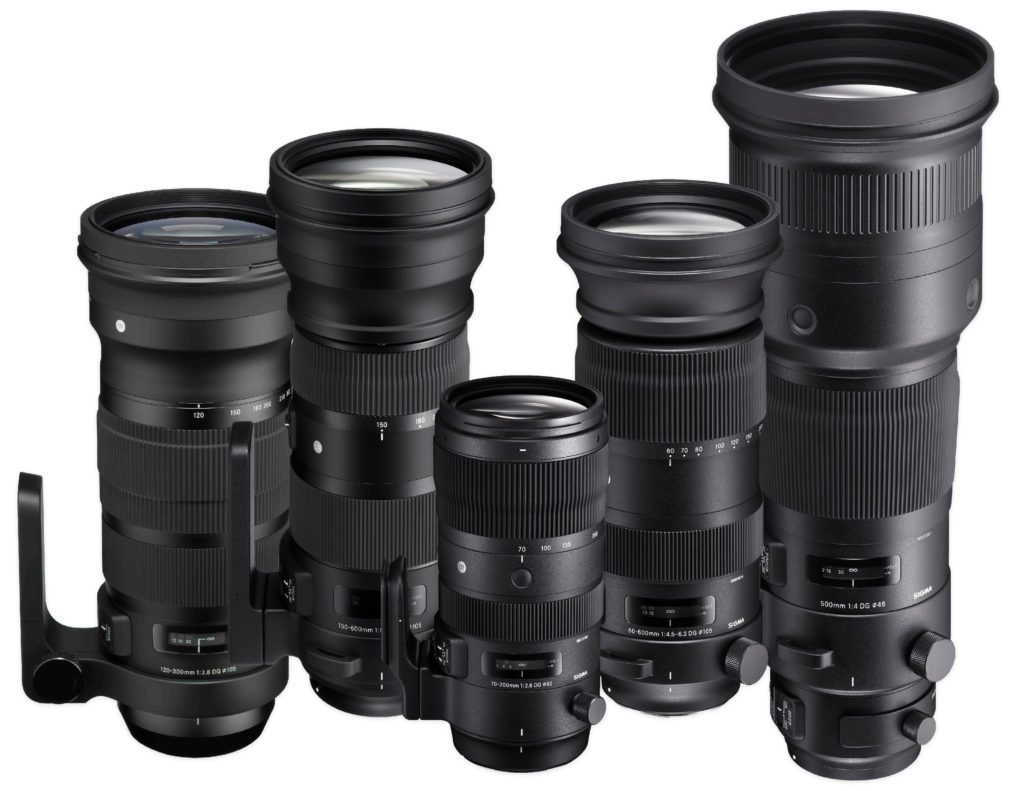

Which SIGMA zoom lenses are right for you depends on your photographic intentions, budgets, and overall size constraints. In this article, we are going to explore many facets of zoom lenses for digital photography and explain the terminology, key features and benefits of the different types of zoom lens. We’re also going to showcase images made with a variety of SIGMA zoom lenses to illustrate key concepts.
Zoom Ratio, and Constant-Aperture or Variable-Aperture Zoom Lenses
Zoom lenses always feature two focal lengths in the name which indicate the shortest and longest focal lengths in relation to the 35mm/full-frame sensor. To determine the overall zoom ratio of the lens, simply divide the longest focal length by the shortest. For example, the SIGMA 18-35mm F1.8 DC HSM | Art and the 8-16mm F3.5-4.5 are both examples of 2x zoom lenses: 35 divided by 16 equals 1.95, and 16 divided by 8 equals 2. (It is common practice to round to the nearest whole number or major fraction.)
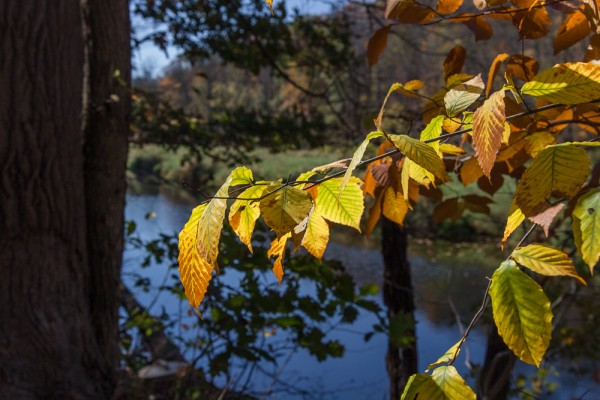
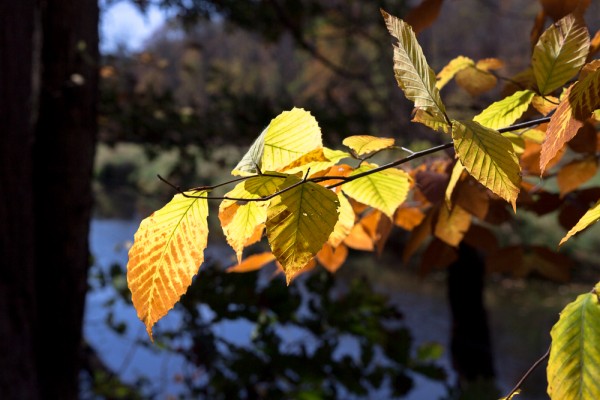


The 120-300mm F2.8 DG OS HSM | Sports is a 2.5x zoom lens and the 70-200mm F2.8 DG OS HSM | Sports is a 2.8 zoom lens. Zoom ratio only relates to the difference between the shortest and longest focal lengths, so the 150-600mm F5-6.3 Contemporary and Sports lenses are 4x zoom lenses, while the 60-600mm F4.5-6.3 DG OS HSM | Sports is a 10x high ratio zoom lens. All three of of these lenses offer the same maximum telephoto focal length, but the 60-600mm offers a much longer zoom range.
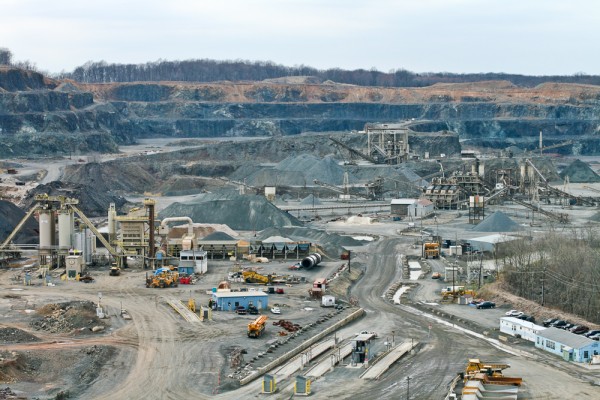
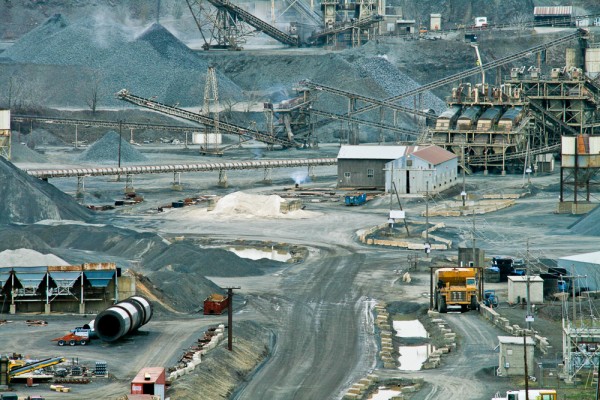


So, you can have a wide to short telephoto zoom lens with a higher overall zoom ratio than a telephoto to super telephoto zoom lens. For example, the 24-105mm F4 DG OS HSM | Art is a 4.3x zoom, while the huge 300-800mm F5.6 EX DG HSM lens is a 2.6x zoom lens, and the SIGMA 18-300mm F3.5-6.3 DC MACRO OS HSM | Contemporary is a wide to telephoto zoom lens with a very high zoom ratio. (We’ll let you do the math on this one!)
Zoom lenses also come in two main varieties: constant-aperture and variable-aperture. Each type has its strengths and purposes, depending on what is most critical to the photographer. When you look at the name of a zoom lens, if there is only a single aperture given, this is a constant aperture zoom lens. If there are two F-stops named with a dash in between, this is a variable aperture zoom lens.
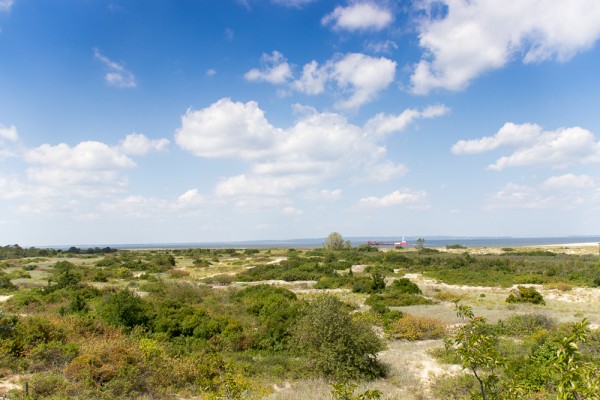
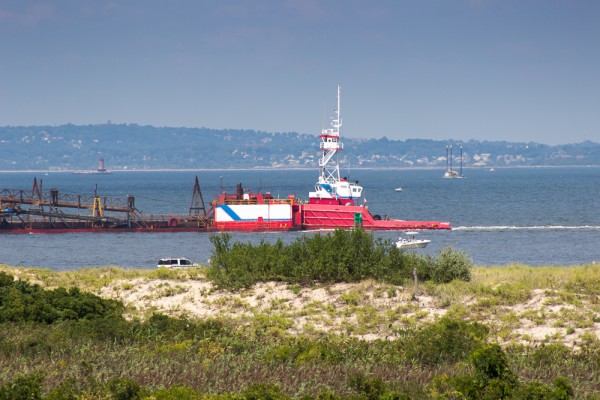


Constant-Aperture zoom lenses keep the same maximum aperture throughout the entire focal range. So, for example, the 120-300mm F2.8 EX DG OS HSM | Sports and the 24-105mm F4 DG OS HSM | Art are both constant aperture zoom lenses. The key advantage of constant aperture zoom lenses is that you do not lose any light-gathering power as the focal length increases. This is helpful in challenging lighting situations, where the extra F-stops allow for faster shutter speeds. Autofocus operations inside a camera’s body also depend on the amount of light coming through the lens.
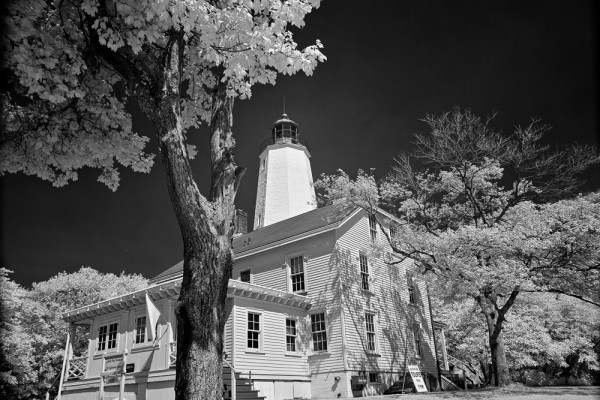

For photographers who want to shoot wide-open in manual exposure mode, this also means you won’t be underexposing your shots as you zoom out, since the F-stop remains constant. Same goes for off-camera strobes—there doesn’t need to be any adjustments as you zoom to recompose with a constant aperture zoom lens.
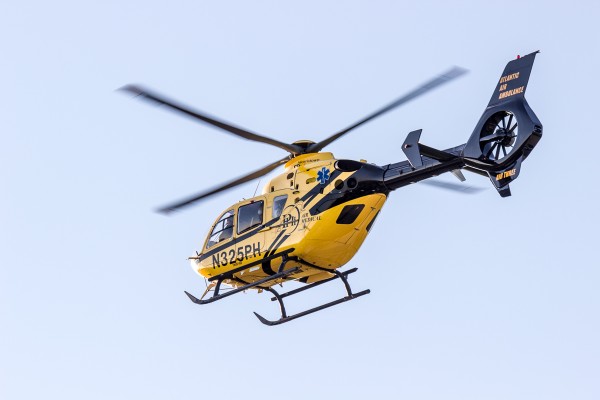

However, constant-aperture zoom lenses are limited in total zoom range: the 24-105mm F4 DG OS HSM | Art is the highest zoom ratio constant-aperture zoom lens in our catalog. And the demands of optical physics require a lot of big glass to make constant-aperture zooms, especially for the full-frame image circle.

Variable-aperture zoom lenses feature two F-stops in the name, indicating the maximum aperture at the shortest and longest focal distance. This means that the overall light-gathering power of the lens decreases as the focal length increases, leading to slower shutter speeds at longer focal lengths. The benefits of this trade-off include more compact lens designs and higher zoom ratios.
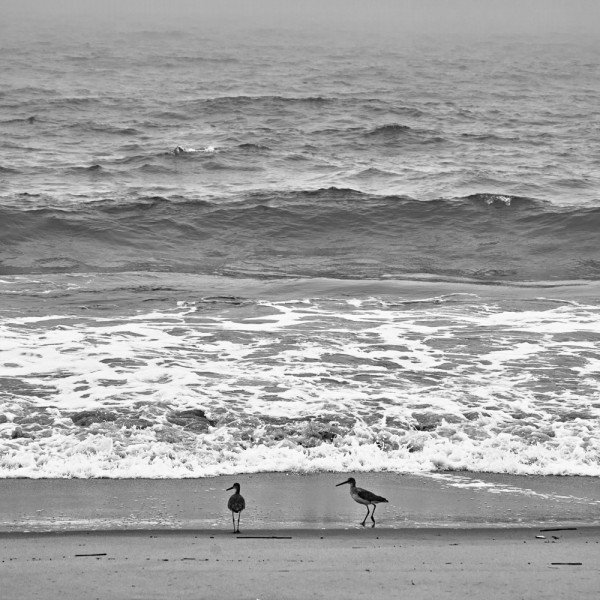
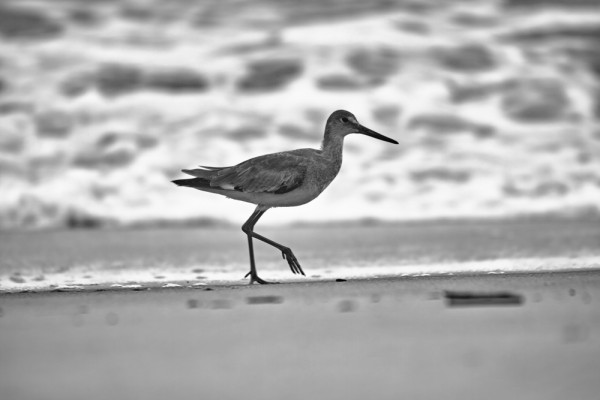


One type of zoom lens is not “better” than the other in an absolute sense—each type of zoom lens has its appeal for different types of photographers and applications, depending on budget, weight considerations, and other variables.
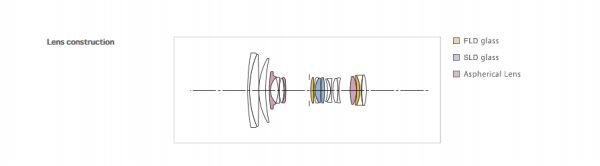
Whichever type of zoom lens it is, the SIGMA lens designers strive to create the best possible lens, incorporating aspherical, SLD and FLD elements as necessary to best transmit the scene to sensor. The optimum optical formula varies depending on the focal lengths, and the goal is to always design the best-performing lens possible within the design parameters.
What is “Optical Stabilizer”?
Many SIGMA zoom lenses feature an Optical Stabilizer, which is a floating lens group that counteracts slight camera movement during image capture—these lenses all have OS in the official lens name. The Optical Stabilizer acts like an invisible tripod, minimizing slight camera movements during longer exposures.
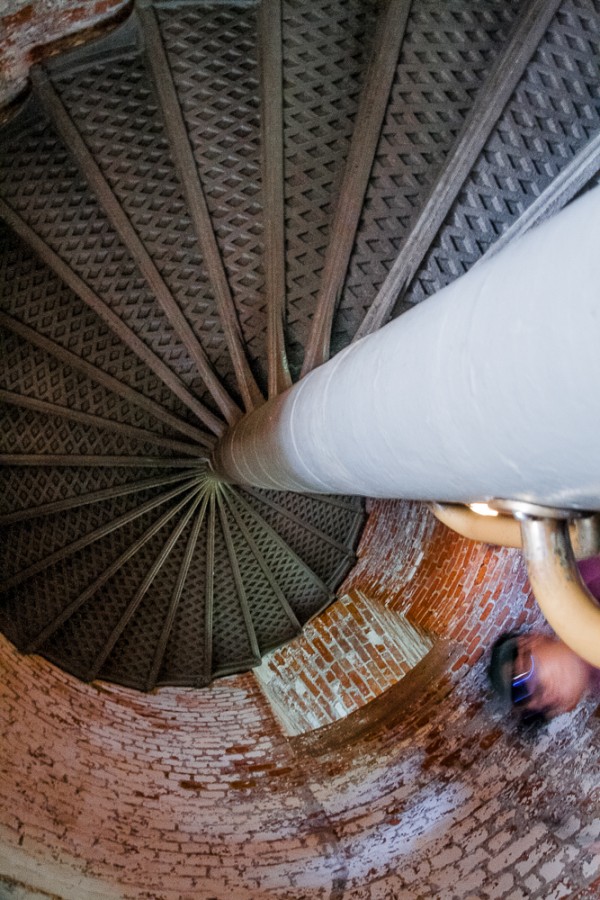

This can help keep handheld shots sharp at slower shutter speeds. The general rule of thumb is that OS can help keep images acceptably sharp for a few stops under the reciprocal of the focal length, so, the effective slowest shutter speed for sharp shots will change as you zoom in or out. We take a long look at OS in this companion piece, if you want to learn more about how, when, and why to use OS when it is offered on a lens.
Why Use Tripod Collars?
Many of the larger SIGMA lenses ship with tripod collars. These tripod collars are paired with the lens because the tripod collar indicates where the center of gravity of the lens and camera resides. If you’ve got a lens that includes a tripod collar, you should always use this for mounting to a tripod, monopod, or other quarter-twenty threaded stabilizing accessory.
Don’t ever use the tripod socket in the base of your camera when paired with a lens that has a tripod collar. You can stress the lens and camera mounts, and while the center of gravity is under the tripod collar mounting point, this can lead to a tripod crashing over!
Versatility is the Key to the Appeal of the Zoom lens
Zoom lenses are designed to offer the photographer a great deal of flexibility in composition and framing without ever having to change lenses, or even physical position, for that matter. All it takes is a quick twist of the zoom ring and the composition can go from the shortest focal distance to the longest for a very different take of the scene presented before your lens. And many SIGMA zoom lenses offer true macro capture at the telephoto end, for close-up capture of tiny objects, adding to the overall versatility.




Of course, as you zoom in or out and recompose, the overall feel of the image can change dramatically, as a lens goes from a wide field of view to standard, or a standard field of view to super telephoto.
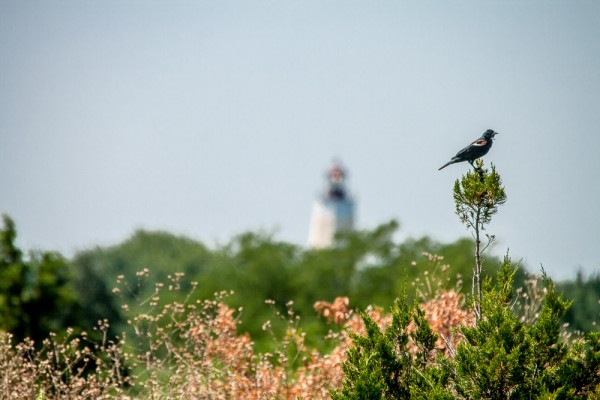


Depth of field gets much more shallow as focal distance increases, even as telephoto compression diminishes the apparent relation between distant objects. The same scene can quickly be seen many different ways with a zoom lens. What’s most important is to choose the focal length and depth of field that will best capture what you are trying to say with your image.







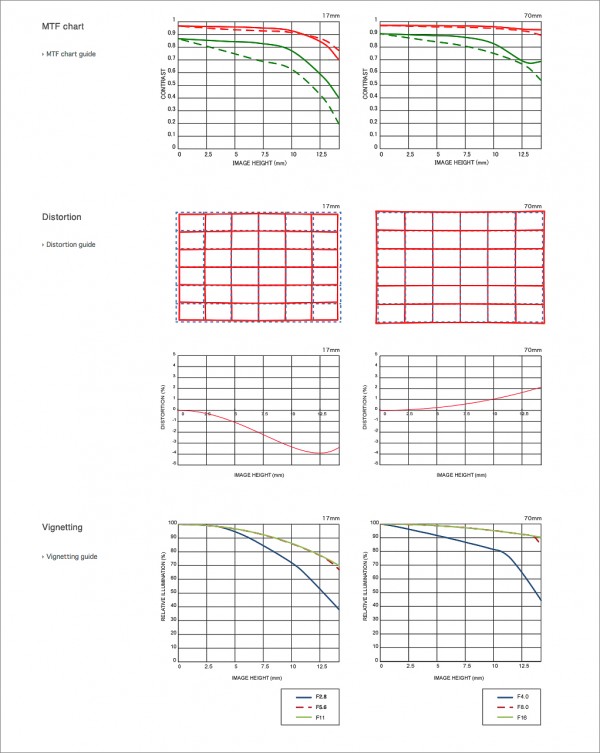
Zoom lens construction technology has come a very long way over the past forty years. And while it is still very typical for many zoom lenses to have some degree of field distortion at one end or the other of the zoom range as well as some slight vignetting at times, the overall image quality straight from the sensor of a modern zoom lens flat-out blows away the results of lenses from a few generations back.
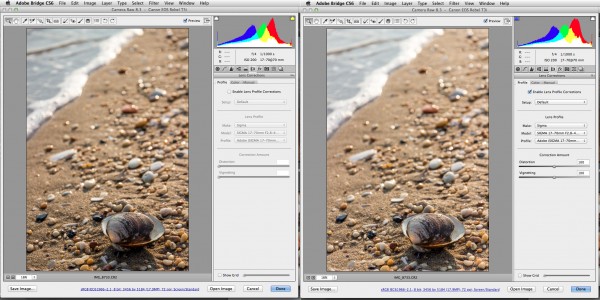
And when you add in the ease of use and accuracy of lens profile corrections that are bundled in most RAW conversion software programs such as the Adobe Camera Raw Engine that is the heart of Lightroom and Bridge/Photoshop toning, many of the historical disputes about prime lenses being the unsurpassed imaging kings don’t resound so absolutely any more.
Crop-Sensor Cameras and Zoom Lenses
SIGMA offers many zoom lenses designed specifically for APS-C DSLRs. These lenses for the smaller image circle are designated with DC in the official name. And every DG lens for full-frame cameras will mount on the APS-C DSLRs in that same mount, too. All SIGMA lens focal lengths are given in relation to the full-frame size, whether it’s a DG or DC lens, so whenever a lens is mounted on an APS-C sensor camera, it is necessary to take the sensor size into account and adjust the apparent focal length and field of view accordingly. For most APS-C DSLRs, it is a 1.5x factor, so the SIGMA 10-20mm F3.5 EX DC HSM lens equates to a 15-30mm F3.5 zoom lens. (10 x 1.5 = 15) – (20 x 1.5 = 30).

This is how it works, and this is how it is. On the shorter end of the focal lengths, it usually feels like APS-C is losing some of the wide-angle capabilities. But lenses like the pair of 10-20mm DC zooms and the 8-16mm F4.5-5.6 ultrawide zooms offer APS-C photographers incredibly wide fields of view that equate to the widest rectilinear fields of view for full-frame ultrawides.

But this smaller sensor also means their is an apparent gain in focal length on the longer side of the zoom range. This means that a 200mm focal length on an APS-C DSLR is more like a 300mm field of view and a 500mm focal length is like 750mm on a full-frame camera. For wildlife photographers, this sensor factor can make distant animals bigger in the frame. And when it comes to full-frame lenses on APS-C DSLRs, the smaller image circle means that the image is captured with incredible sharpness from the center section of the lens.
Zoom Lenses and Macro
Many SIGMA zoom lenses offer a macro capture mode at the longest focal length at magnification ratios between one-third and one-half life sized reproduction. When a SIGMA zoom lens has “MACRO” in the official name, it means that it has a maximum magnification ratio of 1:3 or greater. This means that at the closest focusing distance, a one inch object will be rendered as one-third of an inch (.333 inches) on the sensor. (In the metric system, one centimeter equals 10 millimeters, so a one centimeter object is drawn across 3.3mms on the sensor.)

For many photographers first exploring macro capture, this a great way to get comfortable with the nuances of macro photography. At very close focusing distances, all motion is amplified. For example, a bit of jittery camera movement, and the slight swaying of a flower can mean the difference between having that ladybug perfectly in focus or having the subject drift out of the sharpness zone. Macro takes practice, and if you crave higher magnification than is offered at the far end of a the zoom, SIGMA offers a line of pro-caliber prime macros offer true 1:1 (life-sized) magnification for even more close-up details.
What SIGMA Zoom Lenses are Designed for Mirrorless and DSLR Cameras?
As of April 2020, SIGMA offers two mirrorless-exclusive zoom lenses, the 14-24mm F2.8 DG DN | Art and the 24-70mm F2.8 DG DN Art lenses. Additionally, many DSLR zoom lenses can be adapted to L-mount and Sony E-Mount cameras. Learn much more about which SIGMA lenses fit which camera systems here.
Which Zoom Lens is Right for Me?
Answering the question: “Which zoom lens is right for me?” depends on your photographic intentions. A single zoom lens such as the 18-250mm can cover wide-angle to telephoto, plus macro in a single lens, when traveling light with maximum versatility is the demand. Or a zoom lens like the 120-300mm F2.8 DG OS HSM can offer telephoto prime performance with the added benefit of a zoom range, along with the ultimate in lens customization when paired with the SIGMA-exclusive USB Dock and SIGMA Optimization Pro. The SIGMA 18-35mm F1.8 DC HSM is the world’s first F1.8 zoom lens for APS-C DSLRs and offers image quality that surpasses top-shelf prime lenses in independent lab testing. The pair of SIGMA 150-600mm F5-6.3 DG OS HSM zoom lenses offers incredible full-frame telephoto zoom range in two different designs, with optical stabilization. The SIGMA 17-50mm F2.8 EX DC (OS)* HSM and the 17-70 F2.8-4.0 DC MACRO (OS)* HSM | Contemporary are both fantastic standard zoom upgrades that blow away the standard kit lens that ships with so many DSLRs.
There’s a SIGMA zoom lens that’s right for just about every photographer on any budget. Check out the full lineup here!

